客户端对做后端的我来说,一直是黑盒子般。自从换了Mac,就寻思着什么时候学习学习iOS开发。这几个月断断续续花了时间,先是看了Stanford的cs193p课程,后来又读了<iOS Programming The Big Nerd Ranch Guide>,最后写了个非常简单的App:ToDo。今天这里分享下iOS一些学习笔记,素材取自cs193p的ppt,apple的开发者文档。鉴于我现在iOS水平有限,写得比较浅,大家请见谅。
What’s in iOS?
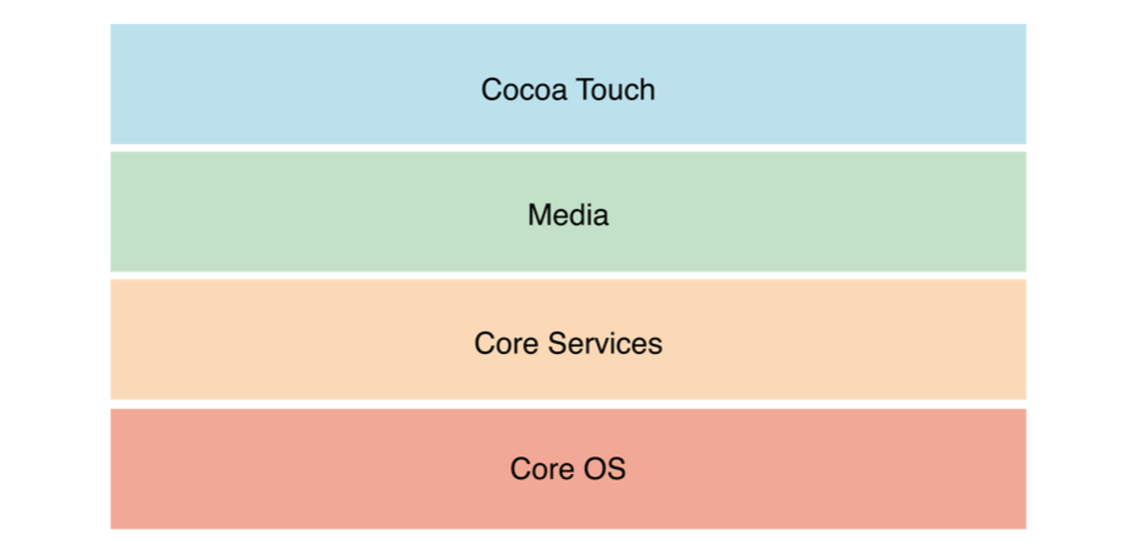
iOS处于底层硬件和app的中间。iOS的整体架构可以划分为四层:Core OS, Core Services, Media, Cocoa Touch
-
Core OS: Contains the low-level features that most other technologies are built upon. Include:OSX Kernel, Mach 3.0, BSD, Sockets, Security, Power Management, Keychain Access, Certificates, File System, Bonjour
-
Core Services: Contains fundamental system services for apps. This layer also contains individual technologies to support features such as location, iCloud, social media, and networking. Include:Collections, Address Book, Networking, File Access, SQLite, Core Location, Net Services, Threading, Preferences, URL Utilities. 我理解是在Core OS基础上封装了一层接口。
-
Media: Contains the graphics, audio, and video technologies you use to implement multimedia experiences in your apps. Include:Core Audio,OpenAL, Audio Mixing, Audio Recording, Video Playback, OpenGL ES, Core Animation.
-
Cocoa Touch: Contains key frameworks for building iOS apps. These frameworks define the appearance of your app. They also provide the basic app infrastructure and support for key technologies such as multitasking, touch-based input, push notifications, and many high-level system services. Include: Multi-Touch, Core Motion, View Hierarchy, Localization, Controls, Alerts, Web View, Map Kit, Image Picker, Camera.
MVC
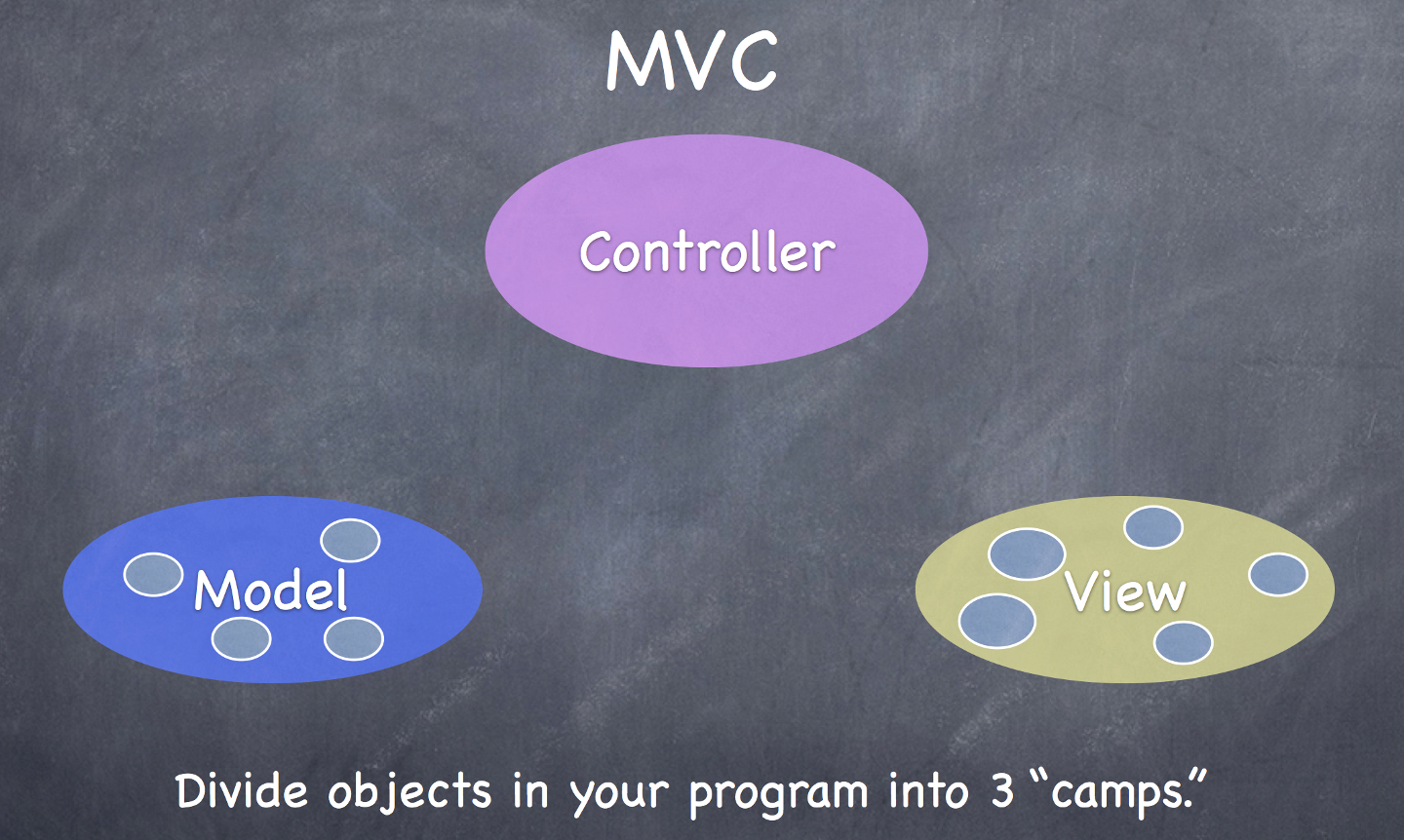
- Model: What your application is (but not how it is displayed)
- Controller: How your Model is presented to the user (UI logic)
- View: Your Controller’s minions
应用程序的逻辑应该放在Model而不是Controller,因为Model = What your application is。
MVC之间的关系
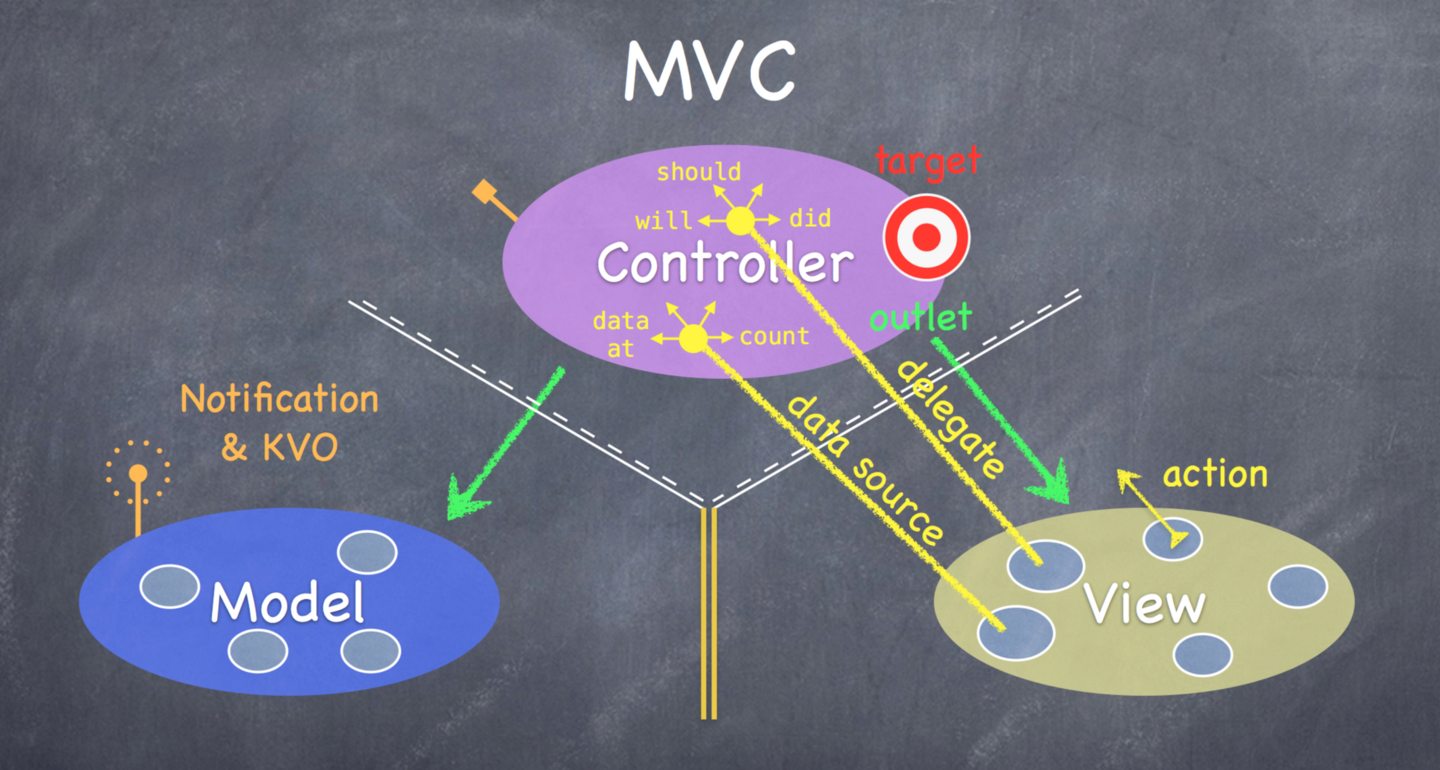
- Controller可以直接访问Model和View(outlet)
- Model和View是完全隔离开的
- View通过protocol的方式(blind and structured)访问Controller,包括:target-action方式,delegate方式和data source方式。
- Model通过notification&KVO(Key Value Observing)将变化通知给Controller
多个MVC的组织
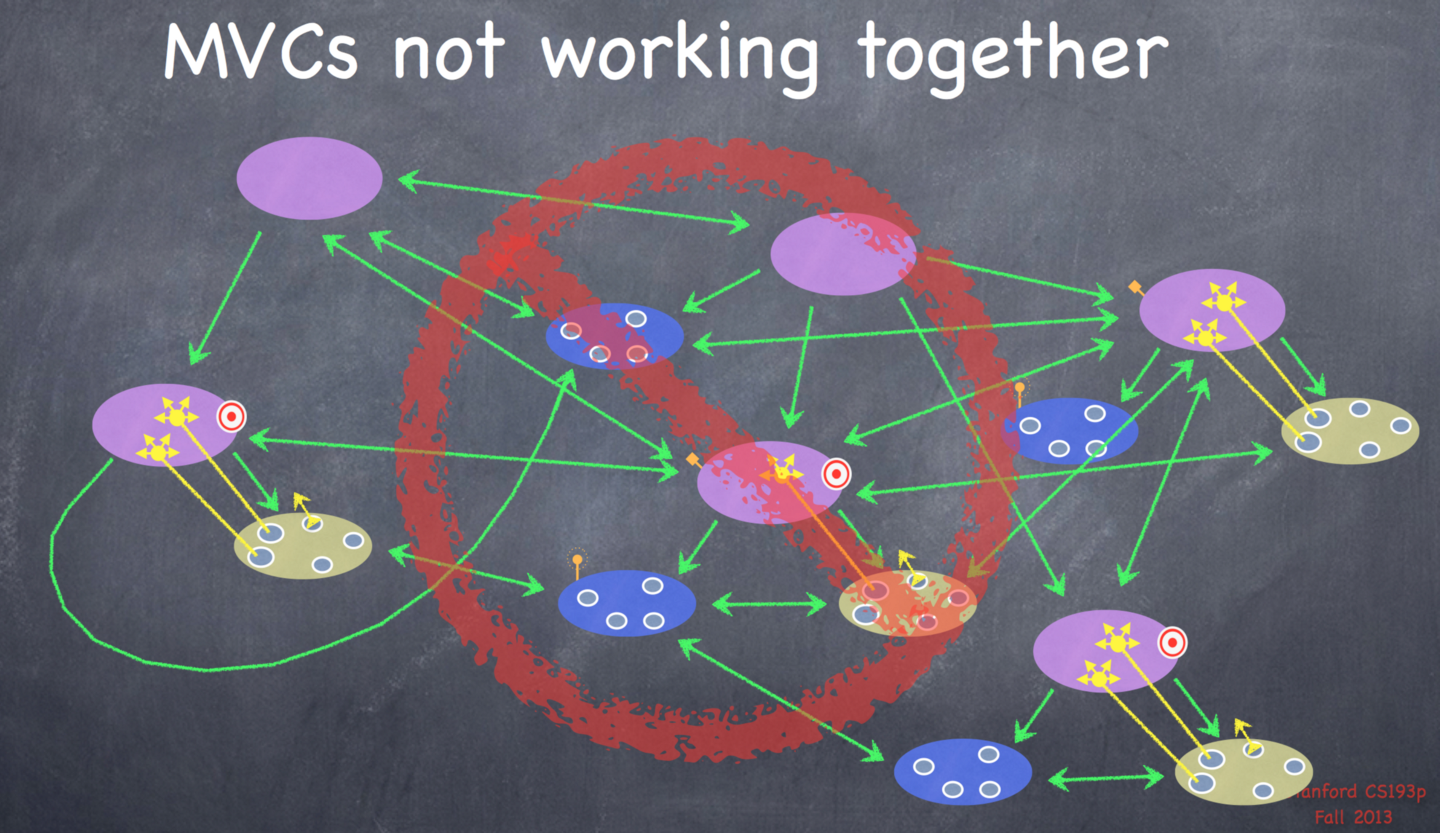
错误的做法:不同模块的communication非常杂乱,难以维护。
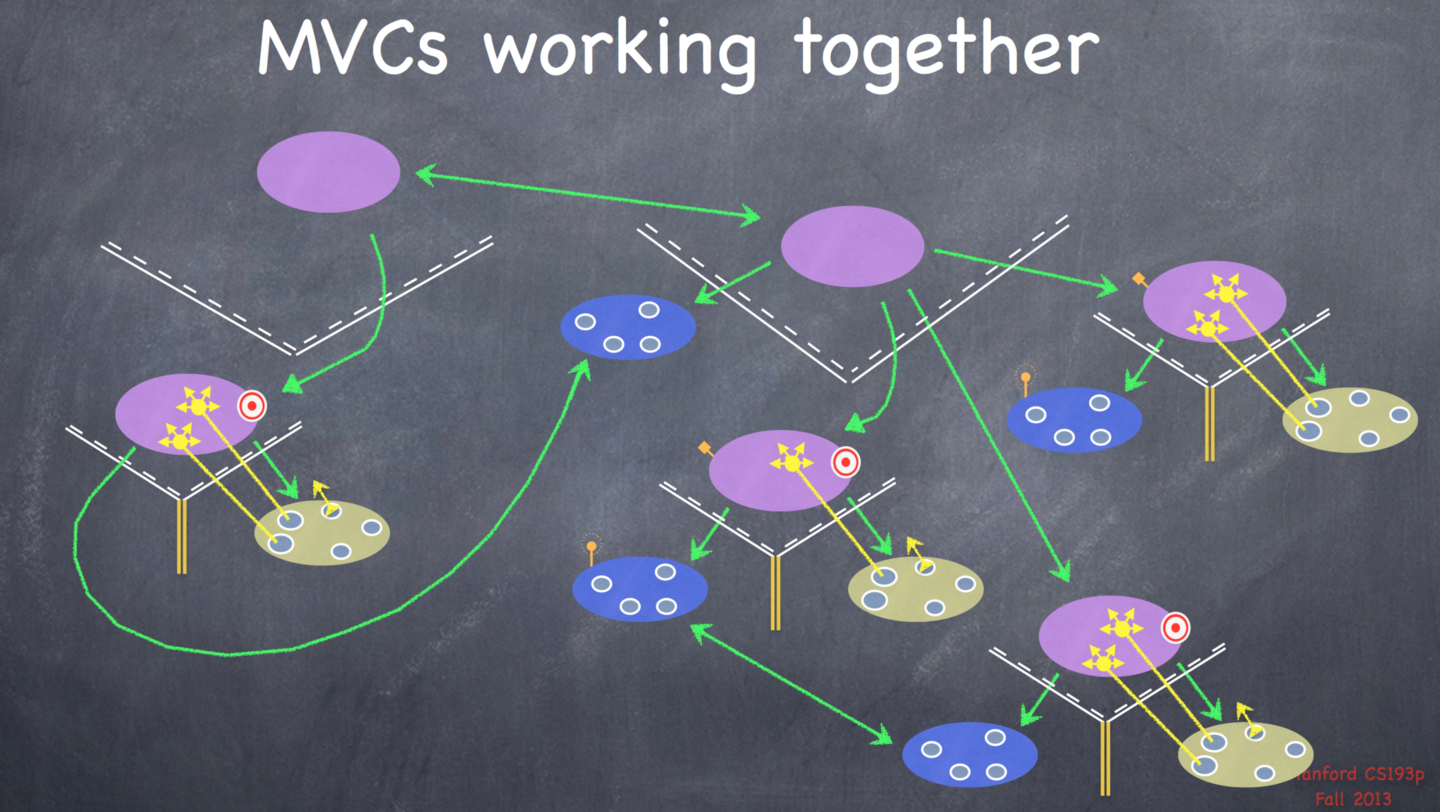
正确的做法:Using MVC as part of the view of another MVC。划分好模块,不同模块间的communication非常少。
Objective-C
面向对象编程的三个原则是:基于消息传递机制,对象分离和多态
- Category
给已存在的类新增新的方法。
//NSObject+HelloWorld.h @interface NSObject (HelloWorld) -(void)HelloWorld; @end //NSObject+HelloWorld.m \#import "NSObject+HelloWorld.h" @implementation NSObject (HelloWorld) -(void)HelloWorld{ NSLog(@"Hello World!"); } @end- Category vs Inheritance: Category用于给一个类新增一个功能,Inheritance用于修改父类的功能。
- Category vs Extension: Extension一般用来隐藏类的私有信息,需要有类的源码才能添加Extension。另外Extension可以添加成员变量,而Category不允许。
- 动态绑定
- Introspection: Asking at runtime what class an object is or what messages can be sent to it.
**isKindOfClass**: returns whether an object is that kind of class (inheritance included) **isMemberOfClass**: returns whether an object is that kind of class (no inheritance) **respondsToSelector**: returns whether an object responds to a given method- Protocols: A syntax that is “in between” id and static typing. Does not specify the class of an object pointed to, but does specify what methods it implements.
//definition file @protocol Foo -(void)someMethod; -(void)methodWithArgument:(BOOL)argument; @property (readonly) int readonlyProperty; // getter (only) is part of this protocol @property NSString *readwriteProperty; // getter and setter are both in the protocol -(int)methodThatReturnsSomething; @end //example file idobj = [[MyClass alloc] init]; </code></pre> Protocols在iOS中的应用包括**delegates** 和 **dataSources**
设计模式
- Target-Action:
Cocoa uses the target-action mechanism for communication between a control and another object. The receiving object—typically an instance of a custom class—is called the target. The action is the message that the control sends to the target.
- Delegation:
Delegation is a simple and powerful pattern in which one object in a program acts on behalf of, or in coordination with, another object. The delegating object keeps a reference to the other object—the delegate—and at the appropriate time sends a message to it.
- Date Source:
A data source is almost identical to a delegate. The difference is in the relationship with the delegating object. Instead of being delegated control of the user interface, a data source is delegated control of data. The delegating object, typically a view object such as a table view, holds a reference to its data source and occasionally asks it for the data it should display.
- KVO
Key-value observing is a mechanism that enables an object to be notified directly when a property of another object changes.
内存管理
iOS使用Automatic Reference Counting来做内存管理。ARC在编译期会分析代码,确定对象的生命周期,在相应的位置自动加上retain和release。