本文是学习Coursera Programming Language课程的学习笔记,文章内容及代码均取自课程材料。
一. 声明式编程和命令式编程
声明式编程(Declarative Programming)
Building the structure and elements of computer programs, that expresses the logic of a computation without describing its control flow.
命令式编程(Imperative Programming)
Describes computation in terms of statements that change a program state.
左图为 Declarative Programming 范式,右图为 Imperative Programming 范式:

二. 函数式编程
三大特性:
- No Mutation
- First Class Function
- Tail Recursion Optimization
1. No Mutation
知乎上《什么是函数式编程思维》其中一个回到写得很好:
函数式编程的本质: 函数式编程中的函数这个术语不是指计算机中的函数,而是指数学中的函数,即自变量的映射。也就是说一个函数的值仅决定于函数参数的值,不依赖其他状态。在函数式语言中,函数作为一等公民,可以在任何地方定义,在函数内或函数外,可以作为函数的参数和返回值,可以对函数进行组合。纯函数式编程语言中的变量也不是命令式编程语言中的变量表示存储状态的单元,而是代数中的变量,即一个值的名称。变量的值是不可变的(immutable),也就是说不允许像命令式编程语言中那样多次给一个变量赋值。
没有 Mutation 带来的好处:
- No code can ever distinguish aliasing vs. identical copies
- No need to think about aliasing: focus on other things
- Can use aliasing, which saves space, without danger
2. How to build bigger types
3 most important type building-blocks in any language
- Each of: A t value contains values of each of t1 t2 … tn
- One of: A t value contains values of one of t1 t2 … tn
- Self reference: A t value can refer to other t values
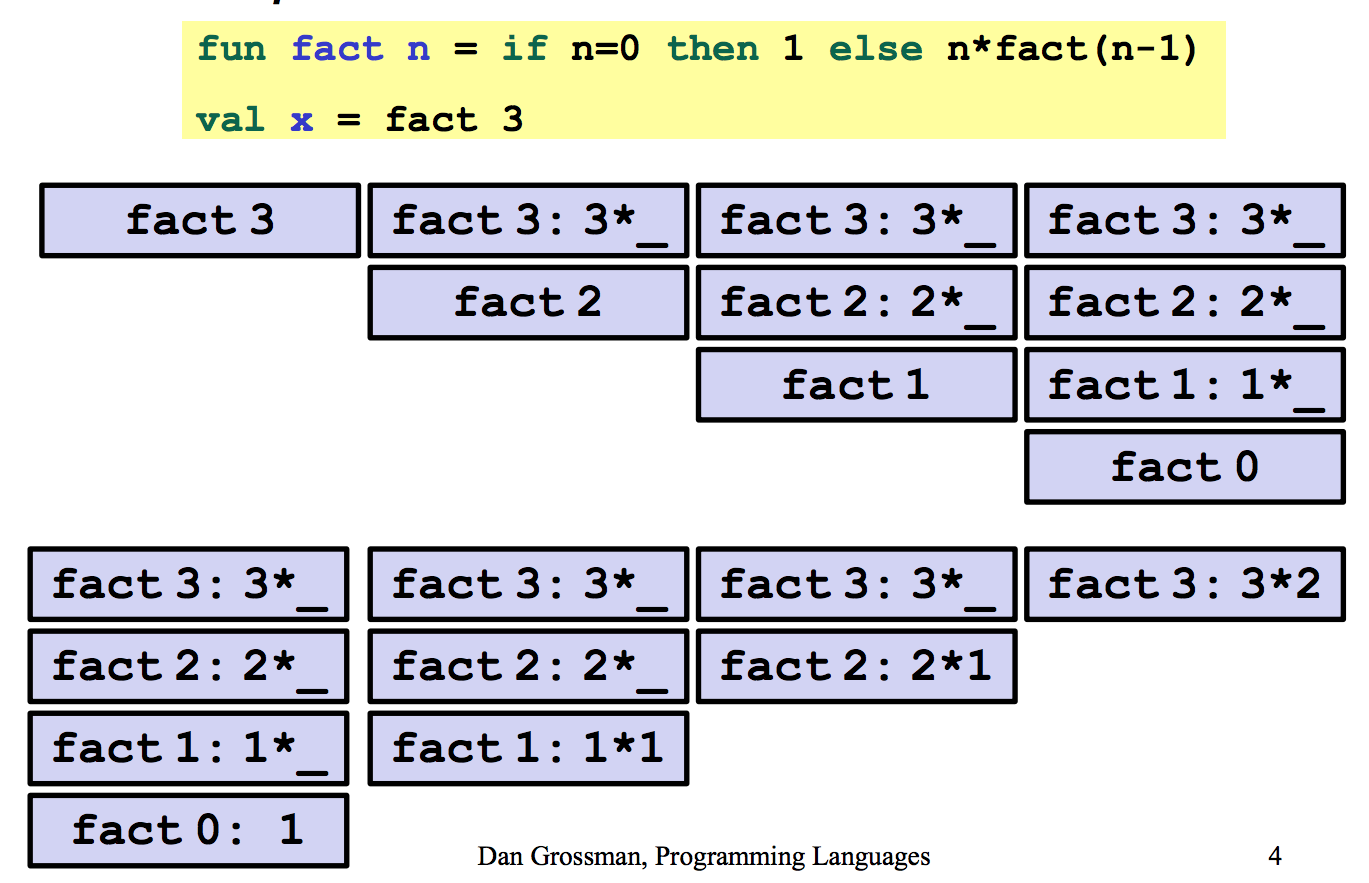
3. Tail Recursion and Accumulators
ML recognizes these tail calls in the compiler and treats them differently: pop the caller before the call, allowing callee to reuse the same stack space
非尾递归的调用堆栈
尾递归优化后的调用堆栈

4. Higher Order Function
Map
1
2
3
4
fun map (f,xs) =
case xs of
[] => []
| x::xs’ => (f x)::(map(f,xs’))
Filter
1
2
3
4
5
6
fun filter (f,xs) =
case xs of
[] => []
| x::xs’ => if f x
then x::(filter(f,xs’))
else filter(f,xs’)
Fold
1
2
3
4
fun fold f acc xs =
case xs of
[] => acc
| x::xs’ => fold f (f(acc,x)) xs’
Higher Order Function vs For Loop
Fold is another very famous iterator over recursive structures. This pattern separates recursive traversal from data processing:
- Can reuse same traversal for different data processing
- Can reuse same data processing for different data structures
- In both cases, using common vocabulary concisely communicates intent
遍历函数和处理函数分离,提高复用性。
5. Function Closure
A function value has two parts:
- The code
- The environment that was current when the function was defined
This pair is called a function closure.
6. Abstract Data Types With Closure
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
datatype set = S of { insert : int -> set,
member : int -> bool,
size : unit -> int }
val empty_set =
let
fun make_set xs = (* xs is a "private field" in result *)
let (* contains a "private method" in result *)
fun contains i = List.exists (fn j => i=j) xs
in
S { insert = fn i => if contains i
then make_set xs
else make_set (i::xs),
member = contains,
size = fn () => length xs
}
end
in
make_set []
end
fun use_sets () =
let val S s1 = empty_set
val S s2 = (#insert s1) 34
val S s3 = (#insert s2) 34
val S s4 = #insert s3 19
in
if (#member s4) 42
then 99
else if (#member s4) 19
then 17 + (#size s3) ()
else 0
end
使用 Java 实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
interface Func<B,A> {
B m(A x);
}
interface Pred<A> {
boolean m(A x);
}
class List<T> {
T head;
List<T> tail;
List(T x, List<T> xs) {
head = x;
tail = xs;
}
// * the advantage of a static method is it allows xs to be null
// -- a more OO way would be a subclass for empty lists
// * a more efficient way in Java would be a messy while loop
// where you keep a pointer to the previous element and mutate it
// -- (try it if you do not believe it is messy)
static <A,B> List<B> map(Func<B,A> f, List<A> xs) {
if(xs==null)
return null;
return new List<B>(f.m(xs.head), map(f,xs.tail));
}
static <A> List<A> filter(Pred<A> f, List<A> xs) {
if(xs==null)
return null;
if(f.m(xs.head))
return new List<A>(xs.head, filter(f,xs.tail));
return filter(f,xs.tail);
}
// * again recursion would be more elegant but less efficient
// * again an instance method would be more common, but then
// all clients have to special-case null
static <A> int length(List<A> xs) {
int ans = 0;
while(xs != null) {
++ans;
xs = xs.tail;
}
return ans;
}
}
class ExampleClients {
static List<Integer> doubleAll(List<Integer> xs) {
return List.map((new Func<Integer,Integer>() {
public Integer m(Integer x) { return x * 2; }
}), xs);
}
static int countNs(List<Integer> xs, final int n) {
return List.length(List.filter(
(new Pred<Integer>() {
public boolean m(Integer x) { return x==n; }
}), xs));
}
}
使用 C 实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
typedef struct List list_t;
struct List {
void * head;
list_t * tail;
};
list_t * makelist (void * x, list_t * xs) {
list_t * ans = (list_t *)malloc(sizeof(list_t));
ans->head = x;
ans->tail = xs;
return ans;
}
list_t * map(void* (*f)(void*,void*), void* env, list_t * xs) {
if(xs==NULL)
return NULL;
return makelist(f(env,xs->head), map(f,env,xs->tail));
}
list_t * filter(bool (*f)(void*,void*), void* env, list_t * xs) {
if(xs==NULL)
return NULL;
if(f(env,xs->head))
return makelist(xs->head, filter(f,env,xs->tail));
return filter(f,env,xs->tail);
}
int length(list_t* xs) {
int ans = 0;
while(xs != NULL) {
++ans;
xs = xs->tail;
}
return ans;
}
// clients of our list implementation:
// [the clients that cast from void* to intptr_t are technically not legal C,
// as explained in detail below if curious]
// awful type casts to match what map expects
void* doubleInt(void* ignore, void* i) {
return (void*)(((intptr_t)i)*2);
}
// assumes list holds intptr_t fields
list_t * doubleAll(list_t * xs) {
return map(doubleInt, NULL, xs);
}
// awful type casts to match what filter expects
bool isN(void* n, void* i) {
return ((intptr_t)n)==((intptr_t)i);
}
// assumes list hold intptr_t fields
int countNs(list_t * xs, intptr_t n) {
return length(filter(isN, (void*)n, xs));
}