前言
在之前的文章《浅读 Libco》 粗略的介绍了 libco,这篇文章则重点关注协程上下文切换的实现细节(coctx_swap.S)。
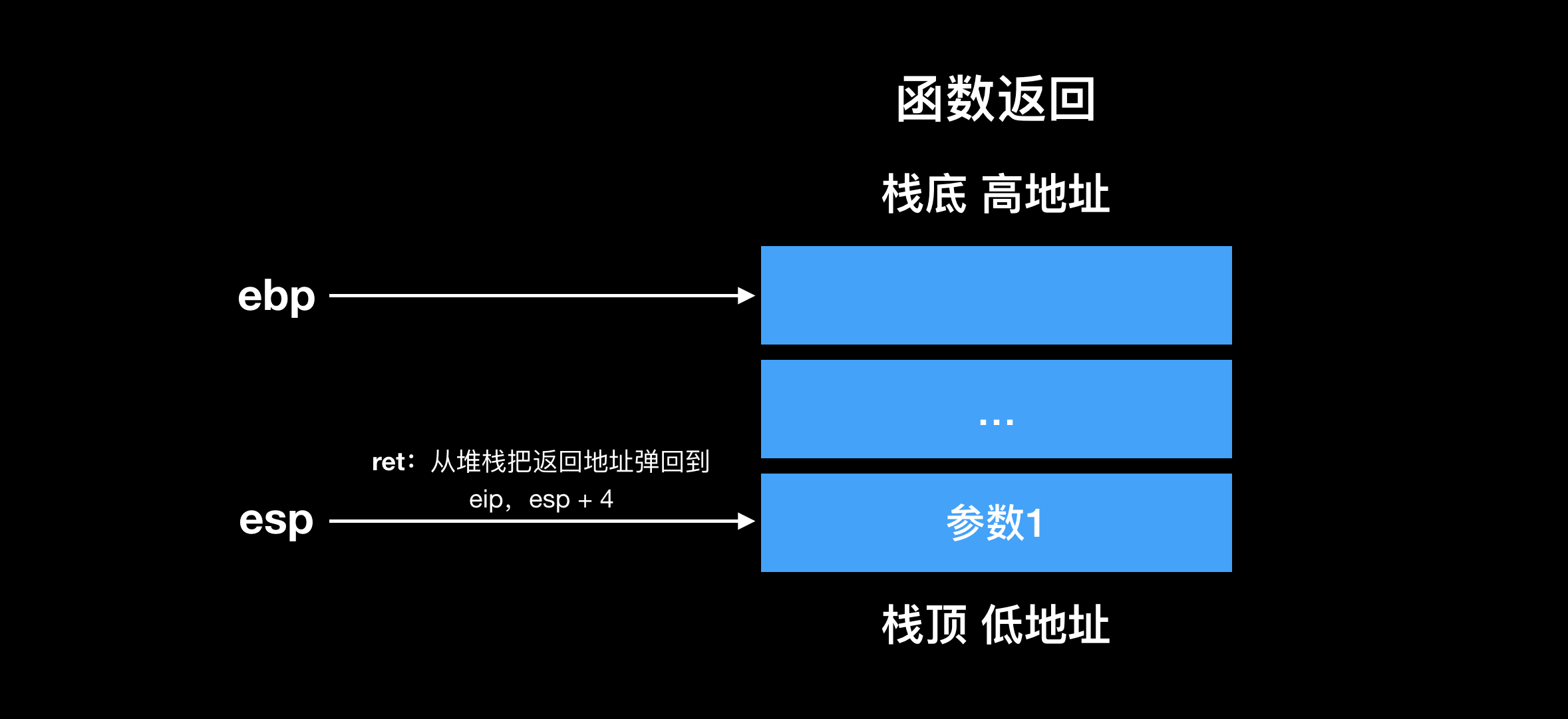
首先回顾下函数调用的 stack frame layout:
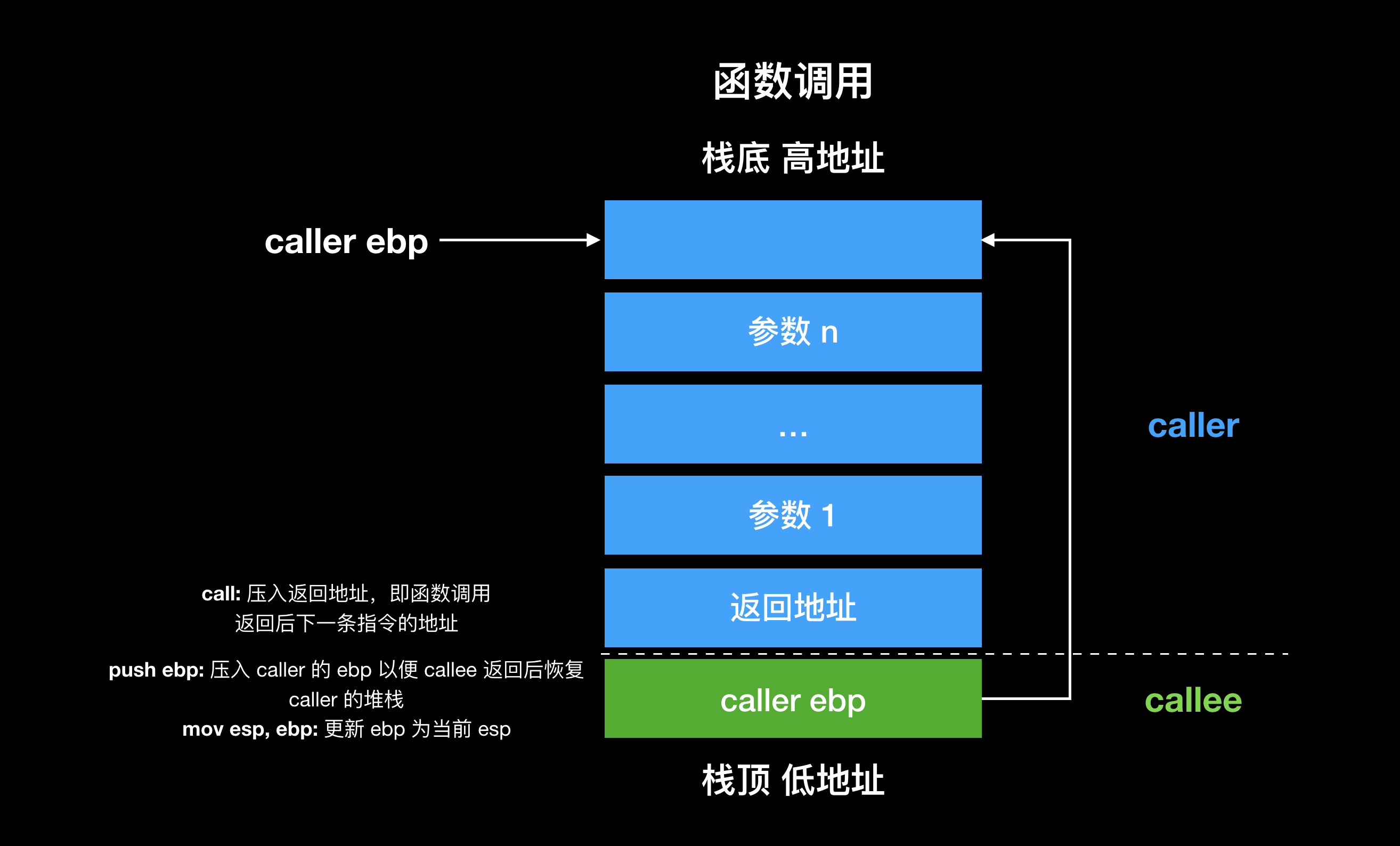
调用子函数时,父函数从右到左将函数入栈,最后将返回地址入栈保存后,跳到子函数的地址执行。子函数压栈保存父函数的 ebp,并将 ebp 设置为当前 esp。子函数通过 ebp + 4 读取参数1,ebp + 8 读取参数2,依次类推。
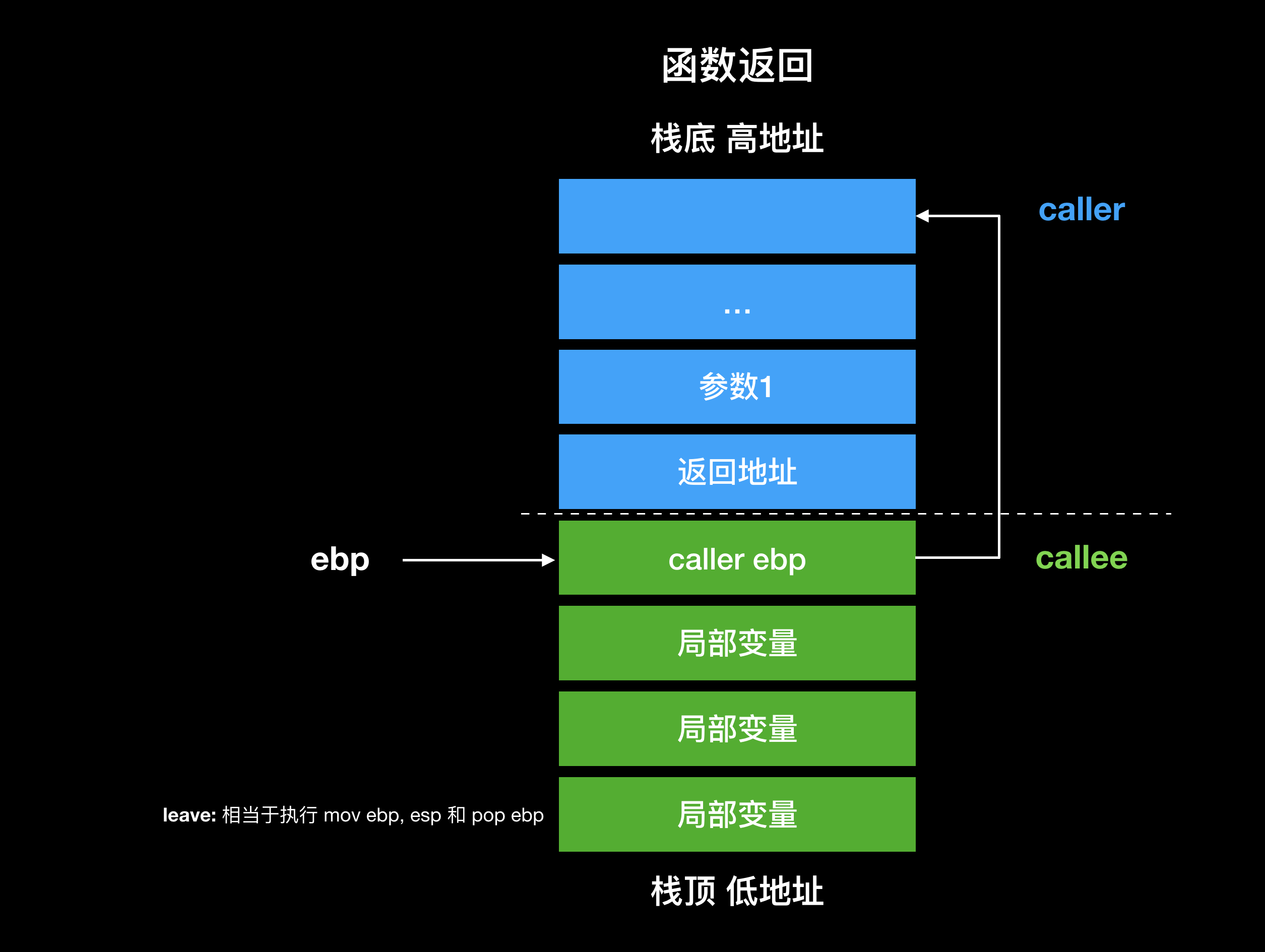
子函数调用返回时先执行 leave 指令,相当于执行 mov ebp, esp 和 pop ebp。
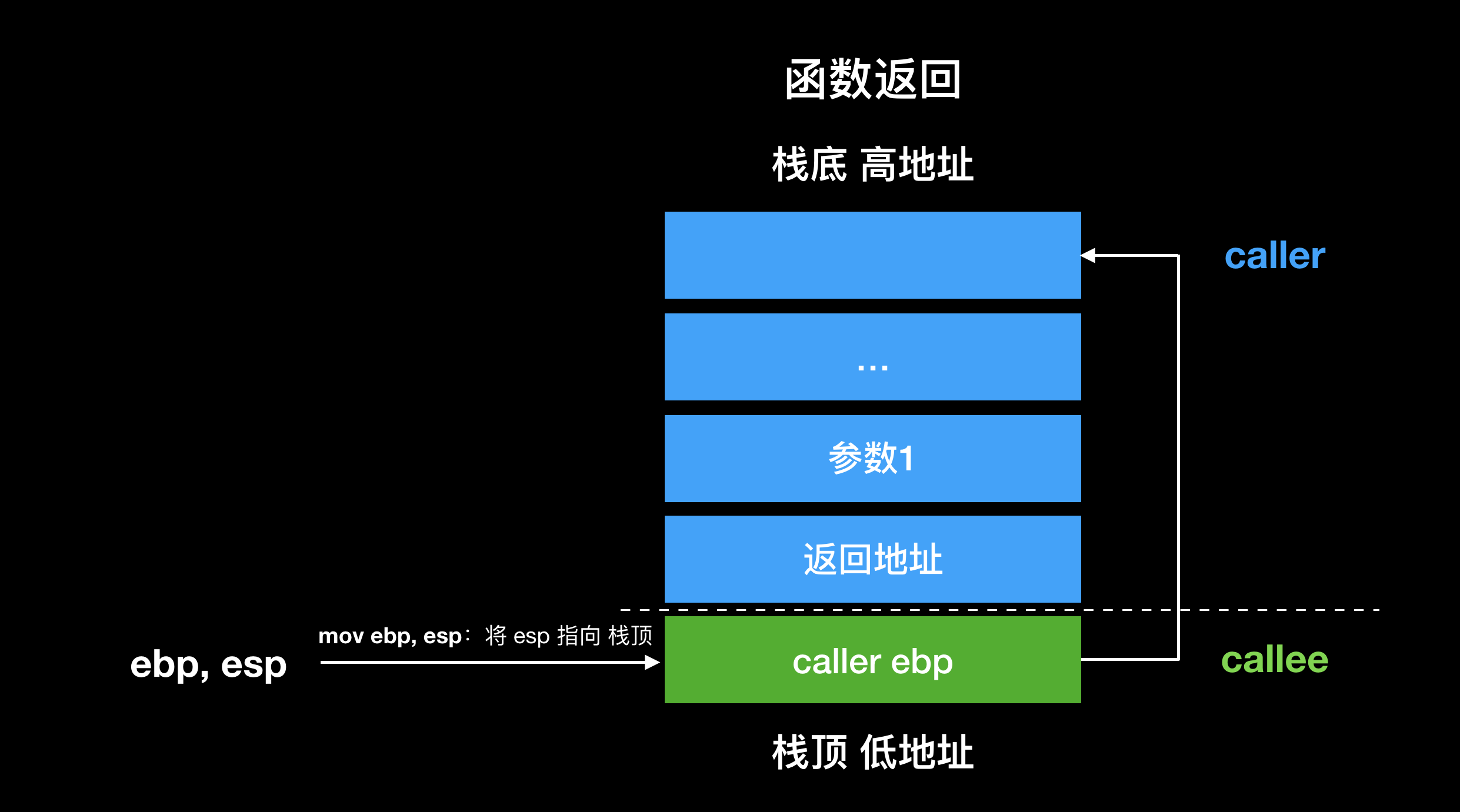
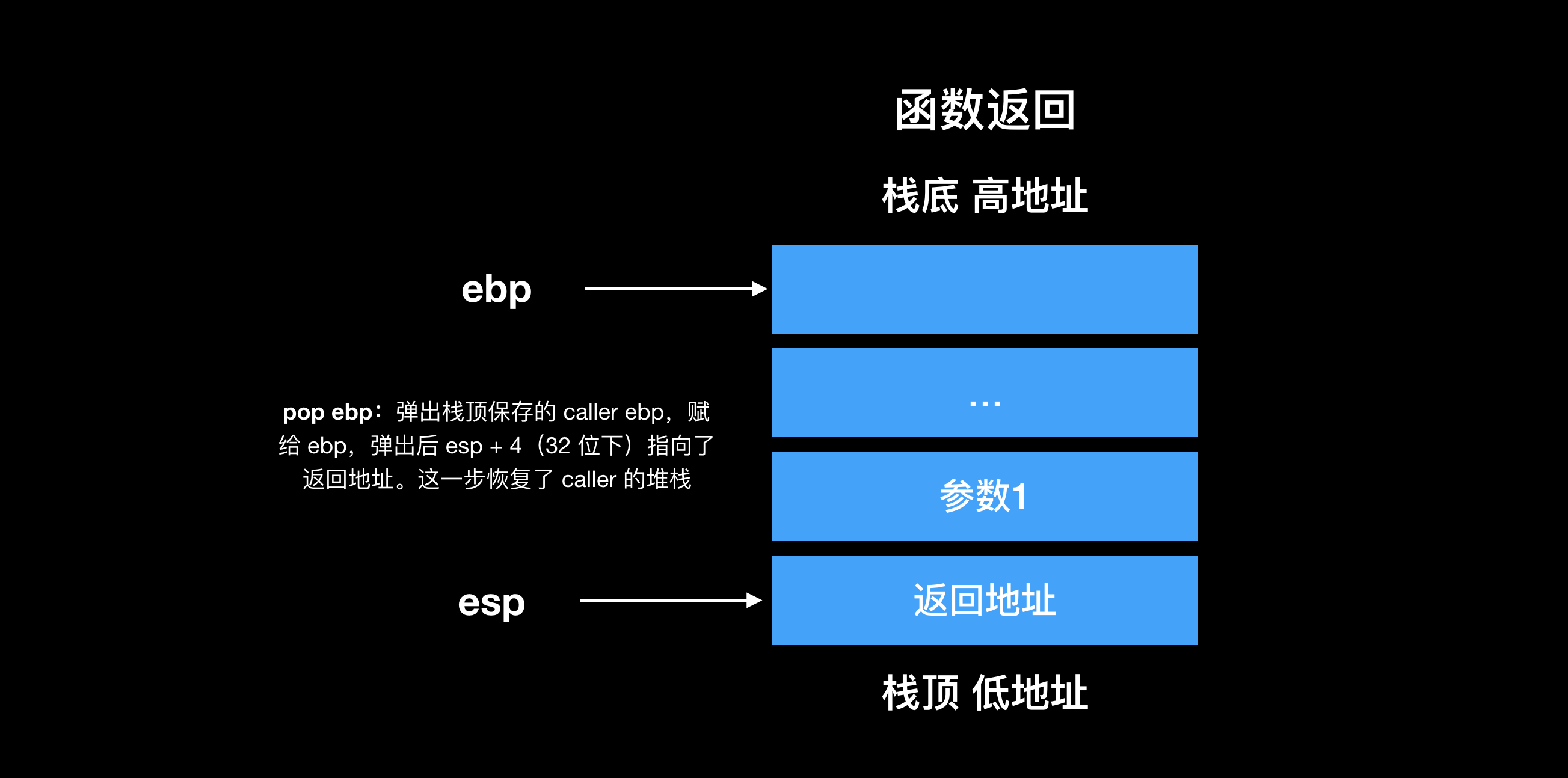
执行 leave 指令后恢复了调用者执行 call 指令前的堆栈,此时 esp 指向的是返回地址。执行 ret 指令,弹出返回地址到 eip,恢复调用者的执行。
co_resume
在之前的文章提到协程的挂起和恢复通过 co_resume 来实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
static int CoRoutineFunc( stCoRoutine_t *co,void * )
{
if( co->pfn )
{
co->pfn( co->arg );
}
co->cEnd = 1;
stCoRoutineEnv_t *env = co->env;
co_yield_env( env );
return 0;
}
void co_resume( stCoRoutine_t *co ) // 恢复 co 协程
{
stCoRoutineEnv_t *env = co->env;
stCoRoutine_t *lpCurrRoutine = env->pCallStack[ env->iCallStackSize - 1 ];
if( !co->cStart )
{
coctx_make( &co->ctx,(coctx_pfn_t)CoRoutineFunc,co,0 );
co->cStart = 1;
}
env->pCallStack[ env->iCallStackSize++ ] = co; // 执行协程的时候压入 pCallStack 栈中
coctx_swap( &(lpCurrRoutine->ctx),&(co->ctx) ); // 恢复 co 协程的上下文
}
这里 coctx_make 函数创建新协程的上下文:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
// 对应 CoRoutineFunc 的两个参数,s1 即 stCoRoutine_t *co,s2 即 void*
struct coctx_param_t
{
const void *s1;
const void *s2;
};
struct coctx_t
{
#if defined(__i386__)
void *regs[ 8 ];
#else
void *regs[ 14 ];
#endif
size_t ss_size;
char *ss_sp;
};
int coctx_make( coctx_t *ctx,coctx_pfn_t pfn,const void *s,const void *s1 )
{
// make room for coctx_param
char *sp = ctx->ss_sp + ctx->ss_size - sizeof(coctx_param_t);
sp = (char*)((unsigned long)sp & -16L); // 16字节对齐
coctx_param_t* param = (coctx_param_t*)sp ;
param->s1 = s;
param->s2 = s1;
memset(ctx->regs, 0, sizeof(ctx->regs));
ctx->regs[ kESP ] = (char*)(sp) - sizeof(void*); // 32位下 regs[ kESP ] 即 regs[7],(char*)(sp) - sizeof(void*) 预留了返回地址的空间
/*
ss_sp 是在堆上分配的,地址从低到高增长,而栈是从高到低增长,这里要转下
高地址
|pading| <- ss_sp + ss_size
|s2 |
|s1 | <- sp
------
|void* | <- ctx->regs[ kESP ] 这个返回地址只是预留空间,不需要填。因为 CoRoutineFunc 函数执行完了表示该协程已经跑完,将其 end 标记位置1(co->cEnd = 1)并调用 co_yield_env 切出。不需要再回到该协程来所以也不需要记录调用 CoRoutineFunc 后的返回地址了。这里为返回地址预留空间的目的在于:参照前言中函数调用的 stack frame layout 图。函数调用压入参数后还需要压入返回地址,这样才能按照约定 ebp + 4 读取参数1,ebp + 8 读取参数2
------
| |
低地址 ------ <- ss_sp
*/
ctx->regs[ kEIP ] = (char*)pfn; // 32位下 regs[ kEIP ] 即 regs[0] 保存 pfn 的地址 也就是 CoRoutineFunc
return 0;
}
co_swap 调用 coctx_swap 来挂起和保存 curr 协程的上下文,恢复 pending 协程的上下文并切换执行流程至 pending 协程:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
void co_swap(stCoRoutine_t* curr, stCoRoutine_t* pending_co)
{
//swap context
coctx_swap(&(curr->ctx),&(pending_co->ctx) );
//stack buffer may be overwrite, so get again;
stCoRoutineEnv_t* curr_env = co_get_curr_thread_env();
...
}
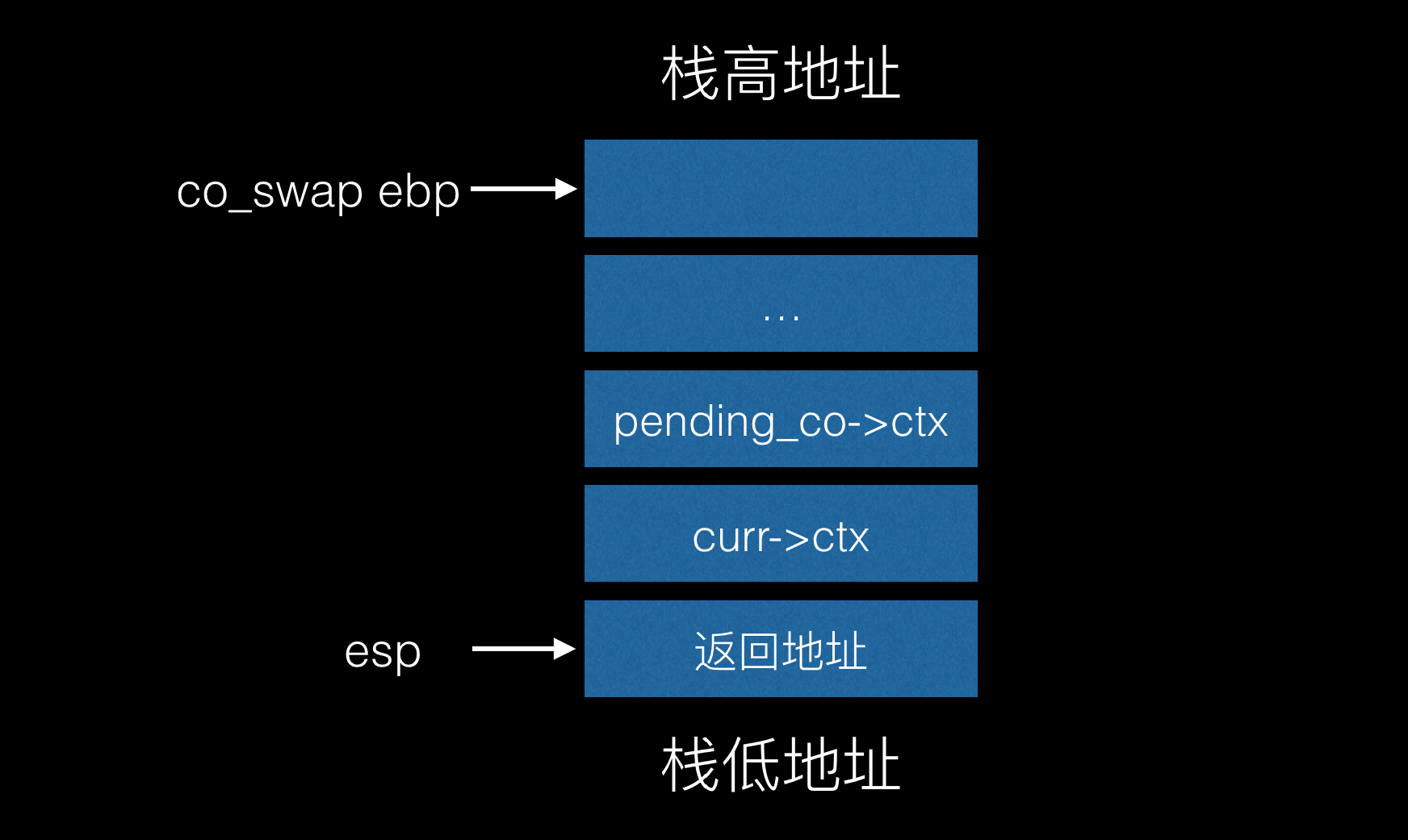
进入 coctx_swap 前 stack frame layout 如下图:
coctx_swap
下面是 coctx_swap 的汇编代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
leal 4(%esp), %eax // 由上图可以看出此时 esp 指向返回地址,esp + 4 即返回地址 + 4(也指向 curr->ctx 的地址),保存在 %eax
movl 4(%esp), %esp // 将 esp 移到指向 curr->ctx
/*
此时 stack layout 如下:
对应的 ESP 地址,此时 ESP 已经指向了第一个参数 curr->ctx,为 coctx_t 结构
| *ss_sp |
| ss_size |
| regs[7] |
| regs[6] |
| regs[5] |
| regs[4] |
| regs[3] |
| regs[2] |
| regs[1] |
| regs[0] | <---ESP
----------
*/
leal 32(%esp), %esp // 将esp上移 32 个字节
/*
| *ss_sp |
| ss_size |
| regs[7] | <---ESP
| regs[6] |
| regs[5] |
| regs[4] |
| regs[3] |
| regs[2] |
| regs[1] |
| regs[0] |
*/
pushl %eax // curr->ctx->regs[7] = %eax 保存返回地址 + 4,即 curr->ctx 的地址
pushl %ebp // curr->ctx->regs[6] = %ebp
pushl %esi // curr->ctx->regs[5] = %esi
pushl %edi // curr->ctx->regs[4] = %edi
pushl %edx // curr->ctx->regs[3] = %edx
pushl %ecx // curr->ctx->regs[2] = %ecx
pushl %ebx // curr->ctx->regs[1] = %ebx
pushl -4(%eax) // curr->ctx->regs[0] = 返回地址 注:%eax - 4 = %old_esp 即返回地址,也就是 co_swap 函数调用后的下一个指令的地址,在这个例子为 stCoRoutineEnv_t* curr_env = co_get_curr_thread_env() 这句指令的地址。当前协程调用 co_swap 后被调度走,下次被调度回来时继续执行 regs[0],也就是 co_swap 的下一个指令。
/*
保存寄存器后的 stack layout
| *ss_sp |
| ss_size |
| regs[7] | %eax
| regs[6] | %ebp
| regs[5] | %esi
| regs[4] | %edi
| regs[3] | %edx
| regs[2] | %ecx
| regs[1] | %ebx
| regs[0] | <---ESP返回地址
-----------
*/
movl 4(%eax), %esp // 将 esp 移到 curr->ctx 向上偏移 4 个字节的地址,也即 pending_co->ctx 的地址,
/*
此时的 stack layout(pending_co->ctx)
| *ss_sp |
| ss_size |
| regs[7] |
| regs[6] |
| regs[5] |
| regs[4] |
| regs[3] |
| regs[2] |
| regs[1] |
| regs[0] | <--- ESP 指向第二个参数 pending_co->ctx->regs[0]
-----------
*/
// 依次恢复寄存器
popl %eax // pop from regs[0] regs[0] 保存返回地址
popl %ebx // pop from regs[1]
popl %ecx // pop from regs[2]
popl %edx // pop from regs[3]
popl %edi // pop from regs[4]
popl %esi // pop from regs[5]
popl %ebp // pop from regs[6]
popl %esp // pop from regs[7] 此时 esp 指向 regs[7]
/*
此时的堆栈
| s2 |
| s1 |
| void* | <- ESP
-----------
| |
*/
// 下面这行有点 ticky, esp 此时指向的是返回地址 + 4 的位置,所以这里 push %eax,入栈 %eax 中保存的返回地址,esp 刚好也指向存放该返回地址的位置
pushl %eax
/*
此时的堆栈
| s2 |
| s1 |
| void* |
| 返回地址 | <- ESP
----------
*/
xorl %eax, %eax
ret // ret 指令弹出返回地址,此时 %esp += 4 并跳转到该地址继续执行
/*
此时的堆栈
| s2 |
| s1 |
| void* | <- ESP / EBP
----------
| 返回地址 | 弹出返回地址
在 coctx_make 的情况下,将跳转到 pfn 执行,esp 执行预留的返回地址 void*,此时stack frame layout 和平台函数调用一样,同样通过 %ebp + 4 访问参数1,%ebp + 8 访问参数2
*/
当被调度走的协程再次被调度回来时,从 reg[7] 恢复 esp 寄存器,从 reg[0] 恢复 eip 寄存器。此时 eip 指向调用 co_swap 返回后下一条指令的地址,即 stCoRoutineEnv_t* curr_env = co_get_curr_thread_env(); 的指令地址,esp 指向的是 curr->ctx 参数,也即是恢复到调用 co_swap 前的堆栈,和普通函数调用一样,esp 指向了函数调用的第一个参数,见前言的最后一个图例。