这篇文章主要整体上介绍 etcd-raft 库,包括各个类的作用,类之间的串联。不涉及 raft 算法。先来看看 etcd-raft 几个结构体的定义:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
type raft struct {
id uint64
Term uint64
Vote uint64
// the log
raftLog *raftLog
state StateType
// isLearner is true if the local raft node is a learner.
isLearner bool
votes map[uint64]bool
msgs []pb.Message
// the leader id
lead uint64
tick func()
step stepFunc
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
type raftLog struct {
// storage contains all stable entries since the last snapshot.
storage Storage
// unstable contains all unstable entries and snapshot.
// they will be saved into storage.
unstable unstable
// committed is the highest log position that is known to be in
// stable storage on a quorum of nodes.
committed uint64
// applied is the highest log position that the application has
// been instructed to apply to its state machine.
// Invariant: applied <= committed
applied uint64
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
// unstable.entries[i] has raft log position i+unstable.offset.
// Note that unstable.offset may be less than the highest log
// position in storage; this means that the next write to storage
// might need to truncate the log before persisting unstable.entries.
type unstable struct {
// the incoming unstable snapshot, if any.
snapshot *pb.Snapshot
// all entries that have not yet been written to storage.
entries []pb.Entry
offset uint64
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// node is the canonical implementation of the Node interface
type node struct {
propc chan msgWithResult
recvc chan pb.Message
readyc chan Ready
advancec chan struct{}
tickc chan struct{}
done chan struct{}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
// Ready encapsulates the entries and messages that are ready to read,
// be saved to stable storage, committed or sent to other peers.
// All fields in Ready are read-only.
type Ready struct {
// The current volatile state of a Node.
// SoftState will be nil if there is no update.
// It is not required to consume or store SoftState.
*SoftState
// The current state of a Node to be saved to stable storage BEFORE
// Messages are sent.
// HardState will be equal to empty state if there is no update.
pb.HardState
// ReadStates can be used for node to serve linearizable read requests locally
// when its applied index is greater than the index in ReadState.
// Note that the readState will be returned when raft receives msgReadIndex.
// The returned is only valid for the request that requested to read.
ReadStates []ReadState
// Entries specifies entries to be saved to stable storage BEFORE
// Messages are sent.
Entries []pb.Entry
// Snapshot specifies the snapshot to be saved to stable storage.
Snapshot pb.Snapshot
// CommittedEntries specifies entries to be committed to a
// store/state-machine. These have previously been committed to stable
// store.
CommittedEntries []pb.Entry
// Messages specifies outbound messages to be sent AFTER Entries are
// committed to stable storage.
// If it contains a MsgSnap message, the application MUST report back to raft
// when the snapshot has been received or has failed by calling ReportSnapshot.
Messages []pb.Message
// MustSync indicates whether the HardState and Entries must be synchronously
// written to disk or if an asynchronous write is permissible.
MustSync bool
}
这几个结构体的关系如下图:
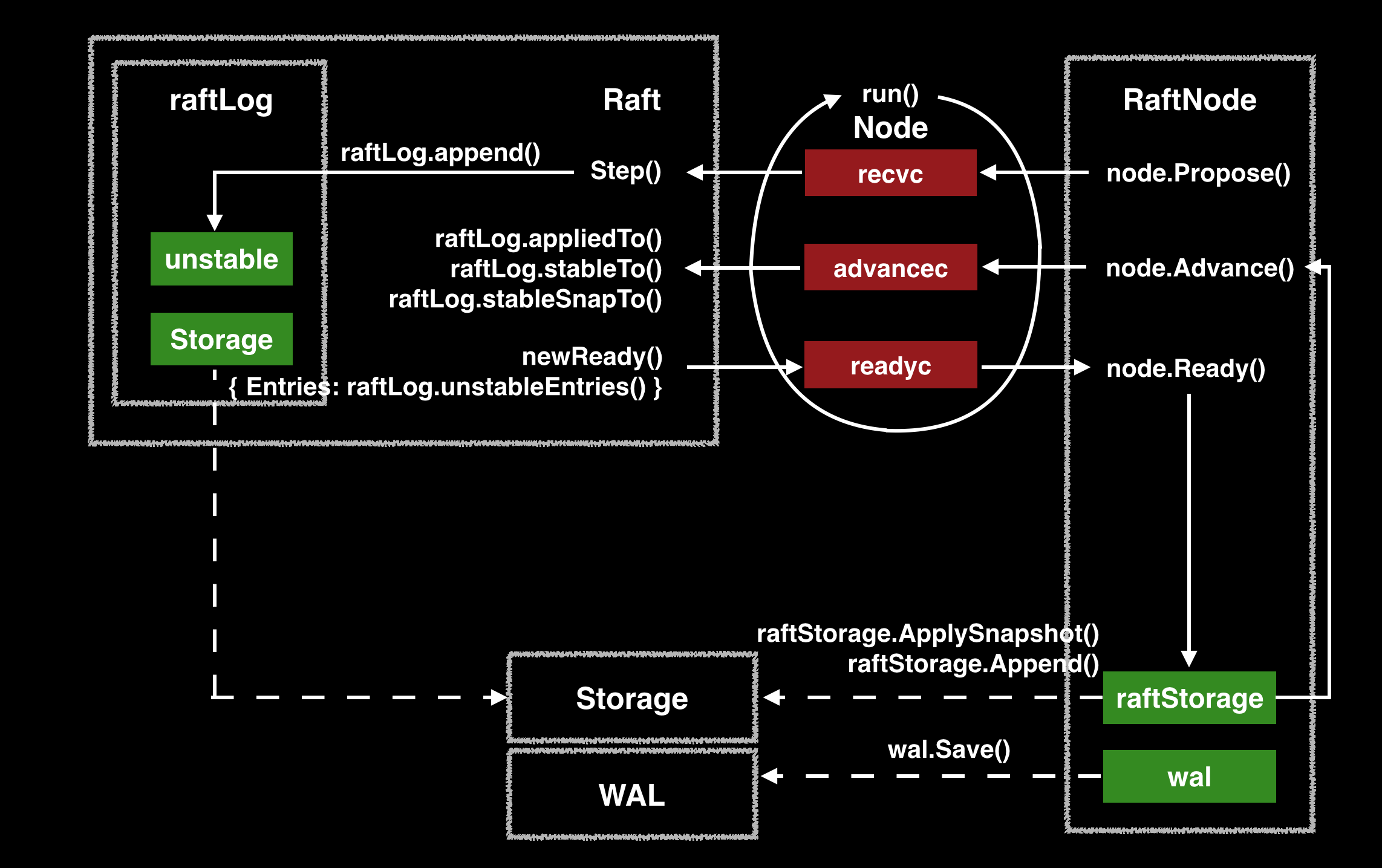
RaftLog 的 Storage 和 RaftNode 的 raftStorage 都是指向同一个 Storage 对象(虚线表示指针)。Storage 在 kvstore 的示例中的实现为 MemoryStorage,可以理解为 WAL 的一个内存缓存。重启时会从 WAL 恢复 MemoryStorage 的数据。整个逻辑由 Node 的 run 方法的 for loop 驱动,从 recvc channel 接收请求,调用 raft 的 Step 函数进行处理。Step 函数会调用 step,step 是函数指针,在节点成为 leader 时将其设置为 stepLeader,节点变成 follower 时设置为 stepFollower。step 处理 append 请求时,会调用 raftLog 的 maybeAppend 方法,最终会把 entries append 到 unstable 中。
在 Node run 方法的 for loop 中,会定期通过 newReady 函数构造 Ready 对象。Ready 包括如下:
- HardState 即 raft 节点的 persistent state
- SoftState 即 raft 节点的 volatile state
- CommittedEntries 即已经 commit 的 log entries,需要应用层 apply 到状态机
- Entries 即 unstable 中的 log entries(未落盘的 log entries)
- Snapshot 即需要持久化的 snapshot
- Messages 即 mailbox,所有还未发送的消息
构造好的 Ready 对象发送到 readyc channel,RaftNode 取出后会做如下处理:
- 持久化 HardState、Entries、Snapshot 到 Storage 和 WAL (
raftStorage.ApplySnapshot()、raftStorage.Append()和wal.Save(rd.HardState, rd.Entries)可以看出 memoryStorage 是 wal 的缓存,写 wal 的同时也写 memoryStorage) - apply CommittedEntries 到状态机
- 广播 Messages
处理完后调用 Node.Advance() 通知 Node Ready 对象处理完毕,准备好接收下一个。
最后看看驱动整个逻辑的 run 方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
func (n *node) run(r *raft) {
var propc chan msgWithResult
var readyc chan Ready
var advancec chan struct{}
var prevLastUnstablei, prevLastUnstablet uint64
var havePrevLastUnstablei bool
var prevSnapi uint64
var rd Ready
lead := None
prevSoftSt := r.softState()
prevHardSt := emptyState
for {
if advancec != nil {
readyc = nil
} else {
// 应用层通知上一个 ready 对象已经处理完毕了 此时 advancec 为 nil
rd = newReady(r, prevSoftSt, prevHardSt)
if rd.containsUpdates() { // 有更新才把 readyc 设为 非空
readyc = n.readyc
} else {
readyc = nil
}
}
select {
case m := <-n.recvc:
// filter out response message from unknown From.
if pr := r.getProgress(m.From); pr != nil || !IsResponseMsg(m.Type) {
r.Step(m)
}
case <-n.tickc:
r.tick()
case readyc <- rd:
if rd.SoftState != nil {
prevSoftSt = rd.SoftState
}
if len(rd.Entries) > 0 {
prevLastUnstablei = rd.Entries[len(rd.Entries)-1].Index
prevLastUnstablet = rd.Entries[len(rd.Entries)-1].Term
havePrevLastUnstablei = true
}
if !IsEmptyHardState(rd.HardState) {
prevHardSt = rd.HardState
}
if !IsEmptySnap(rd.Snapshot) {
prevSnapi = rd.Snapshot.Metadata.Index
}
r.msgs = nil
r.readStates = nil
advancec = n.advancec
case <-advancec:
if prevHardSt.Commit != 0 {
r.raftLog.appliedTo(prevHardSt.Commit)
}
// 应用层处理完了 表示 unstable 的东西不需要了 该清理就清理
if havePrevLastUnstablei {
r.raftLog.stableTo(prevLastUnstablei, prevLastUnstablet)
havePrevLastUnstablei = false
}
r.raftLog.stableSnapTo(prevSnapi)
advancec = nil
}
}
}
还有构造 Ready 对象的 newReady 函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
func newReady(r *raft, prevSoftSt *SoftState, prevHardSt pb.HardState) Ready {
rd := Ready{
Entries: r.raftLog.unstableEntries(),
CommittedEntries: r.raftLog.nextEnts(),
Messages: r.msgs,
}
if softSt := r.softState(); !softSt.equal(prevSoftSt) {
rd.SoftState = softSt
}
if hardSt := r.hardState(); !isHardStateEqual(hardSt, prevHardSt) {
rd.HardState = hardSt
}
if r.raftLog.unstable.snapshot != nil {
rd.Snapshot = *r.raftLog.unstable.snapshot
}
if len(r.readStates) != 0 {
rd.ReadStates = r.readStates
}
rd.MustSync = MustSync(rd.HardState, prevHardSt, len(rd.Entries))
return rd
}