本系列文章是读《coredump问题原理探究》的读书笔记。
函数调用帧
先看一个例子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
// test.cpp
int func(int c, char* s, int off) {
int a = 0x12345678;
int *p = &a;
int res = c + *(s + off);
return *p + res;
}
int main() {
int b = 0x87654321;
return b + func(0x100, "hello", 3);
}
g++ -o test test.cpp 编译后,gdb test 看下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
(gdb) disassemble func
Dump of assembler code for function _Z4funciPci:
0x00000000004005b0 <+0>: push %rbp
0x00000000004005b1 <+1>: mov %rsp,%rbp
0x00000000004005b4 <+4>: mov %edi,-0x14(%rbp)
0x00000000004005b7 <+7>: mov %rsi,-0x20(%rbp)
0x00000000004005bb <+11>: mov %edx,-0x18(%rbp)
0x00000000004005be <+14>: movl $0x12345678,-0x10(%rbp)
0x00000000004005c5 <+21>: lea -0x10(%rbp),%rax
0x00000000004005c9 <+25>: mov %rax,-0x8(%rbp)
0x00000000004005cd <+29>: mov -0x18(%rbp),%eax
0x00000000004005d0 <+32>: movslq %eax,%rdx
0x00000000004005d3 <+35>: mov -0x20(%rbp),%rax
0x00000000004005d7 <+39>: add %rdx,%rax
0x00000000004005da <+42>: movzbl (%rax),%eax
0x00000000004005dd <+45>: movsbl %al,%edx
0x00000000004005e0 <+48>: mov -0x14(%rbp),%eax
0x00000000004005e3 <+51>: add %edx,%eax
0x00000000004005e5 <+53>: mov %eax,-0xc(%rbp)
0x00000000004005e8 <+56>: mov -0x8(%rbp),%rax
0x00000000004005ec <+60>: mov (%rax),%edx
0x00000000004005ee <+62>: mov -0xc(%rbp),%eax
0x00000000004005f1 <+65>: add %edx,%eax
0x00000000004005f3 <+67>: pop %rbp
0x00000000004005f4 <+68>: retq
End of assembler dump.
(gdb) disassemble main
Dump of assembler code for function main:
0x00000000004005f5 <+0>: push %rbp
0x00000000004005f6 <+1>: mov %rsp,%rbp
0x00000000004005f9 <+4>: sub $0x10,%rsp
0x00000000004005fd <+8>: movl $0x87654321,-0x4(%rbp)
0x0000000000400604 <+15>: mov $0x3,%edx
0x0000000000400609 <+20>: mov $0x4006b0,%esi
0x000000000040060e <+25>: mov $0x100,%edi
0x0000000000400613 <+30>: callq 0x4005b0 <_Z4funciPci>
0x0000000000400618 <+35>: mov -0x4(%rbp),%edx
0x000000000040061b <+38>: add %edx,%eax
0x000000000040061d <+40>: leaveq
0x000000000040061e <+41>: retq
End of assembler dump.
可以看到,每个函数调用的开始和结束都有如下指令:
1
2
3
4
5
push %rbp // 入栈 rbp 保存下旧的 rbp,此时 rsp -= 8 (64 位下)
mov %rsp,%rbp // 设置 rbp = rsp
...
pop %rbp // 调用结束 出栈恢复 rbp,此时 rsp += 8 (64 位下)
retq // 把 rbp 指向地址下一个单元的内容放到 rip,此时 rsp += 8 (64 位下)
打个断点验证下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
(gdb) tbreak *0x0000000000400613
Temporary breakpoint 1 at 0x400613
(gdb) r
Starting program: test3
Temporary breakpoint 1, 0x0000000000400613 in main ()
Missing separate debuginfos, use: debuginfo-install glibc-2.17-157.tl2.2.x86_64 libgcc-4.8.5-4.el7.x86_64 libstdc++-4.8.5-4.el7.x86_64
(gdb) i r rsp rbp
rsp 0x7fffffffe460 0x7fffffffe460
rbp 0x7fffffffe470 0x7fffffffe470
(gdb) x /4x $rsp
0x7fffffffe460: 0xffffe550 0x00007fff 0x00000000 0x87654321
si 跟进去,发现 rsp 比之前小了 8 字节(从 0x7fffffffe460 变成了 0x7fffffffe458)。这是因为调用 call 指令会把返回地址(也就是 callq 0x4005b0 <_Z4funciPci> 的下一条指令 mov -0x4(%rbp),%edx 的地址)入栈。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
(gdb) si
0x00000000004005b0 in func(int, char*, int) ()
(gdb) i r rsp rbp
rsp 0x7fffffffe458 0x7fffffffe458
rbp 0x7fffffffe470 0x7fffffffe470
(gdb) x /4x $rsp
0x7fffffffe458: 0x00400618 0x00000000 0xffffe550 0x00007fff
继续执行 push %rbp 之后:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
(gdb) ni
0x00000000004005b1 in func(int, char*, int) ()
(gdb) i r rsp rbp
rsp 0x7fffffffe450 0x7fffffffe450
rbp 0x7fffffffe470 0x7fffffffe470
(gdb) x /4x $rsp
0x7fffffffe450: 0xffffe470 0x00007fff 0x00400618 0x00000000
可以看出 push %rbp 之后 rsp 指向的地址存放了 rbp 的值:
1
0x7fffffffe450: 0xffffe470 0x00007fff
继续执行 mov %rsp,%rbp,此时 rsp 和 rbp 的值一致。rbp 指向上个函数帧的 rbp(本样例为 0xffffe470),rbp 的下个单元指向返回地址(本样例为 0x00400618) ,info symbol 该返回地址可以打印出函数名称(本样例为 main + 35 in section .text of test3)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
(gdb) ni
0x00000000004005b4 in func(int, char*, int) ()
(gdb) i r rsp rbp
rsp 0x7fffffffe450 0x7fffffffe450
rbp 0x7fffffffe450 0x7fffffffe450
(gdb) x /4x $rbp
0x7fffffffe450: 0xffffe470 0x00007fff 0x00400618 0x00000000
(gdb) info symbol 0x00400618
main + 35 in section .text of test3
可以看出函数调用时帧布局:
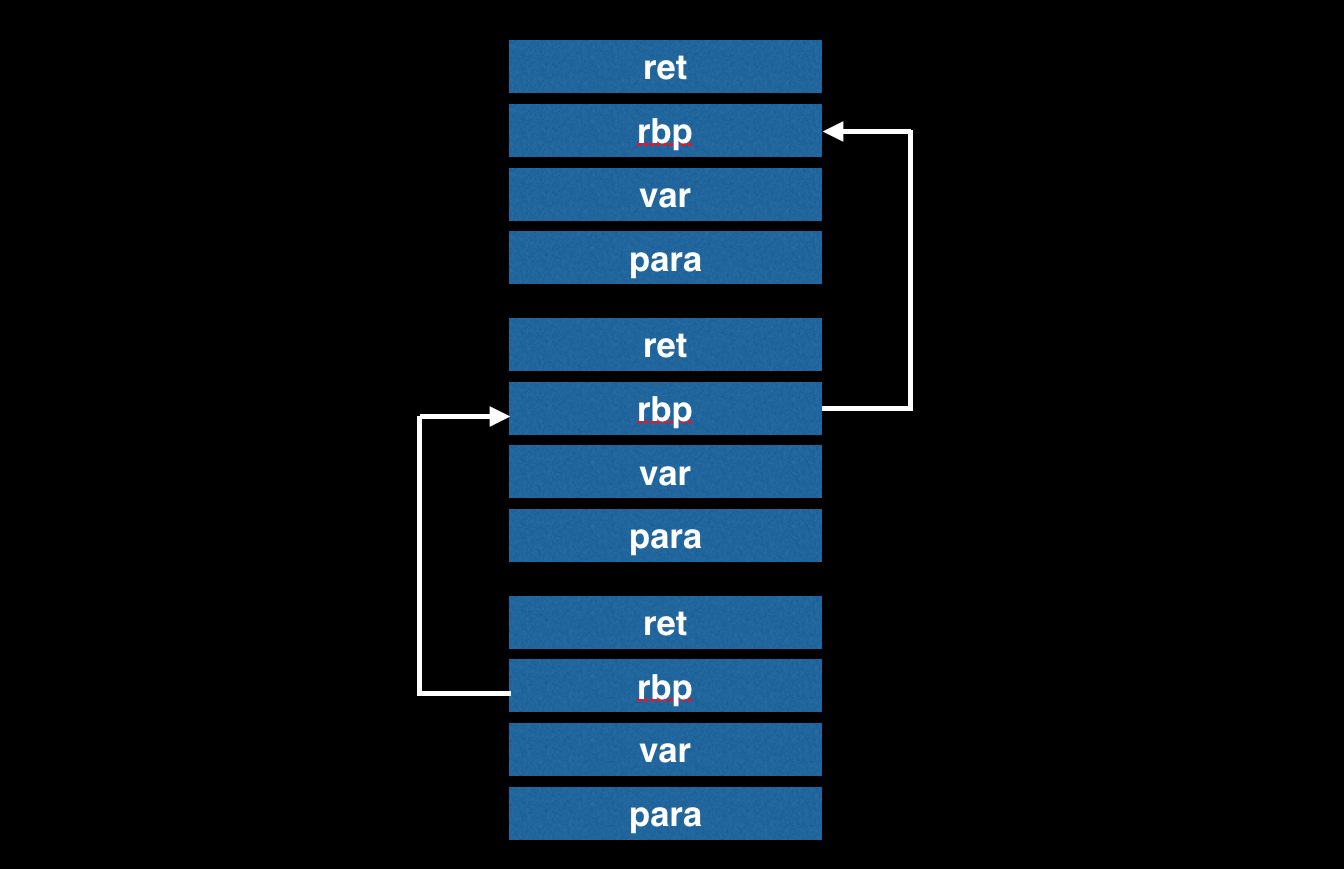
结论:
- rbp 地址大于等于 rsp
- rbp 下一个单元的内容存放返回地址,info symbol 会显示出函数名称
- rbp 所指向的单元是上一帧的 rbp,亦遵守上述两个规则
栈溢出调试
构造一个栈溢出的例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
// test2.cpp
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int overflow(int level, char* str) {
char buff[16];
strcpy(buff, str);
printf("buffer:%s", buff);
return ++level;
}
int wrapper1(int level, char* str) {
return overflow( ++level, str );
}
int wrapper2(int level, char* str) {
return wrapper1(++level, str);
}
int wrapper3(int level, char* str) {
return wrapper2(++level, str);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if ( argc < 2 ) {
return -1;
}
return wrapper3(0, argv[1]);
}
执行 ./test2 WeAreHumanBeingsNothingCanNotStopUsWe core 掉。gdb coredump 文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
(gdb) bt
#0 0x0000000000400680 in overflow(int, char*) ()
#1 0x6f7453746f4e6e61 in ?? ()
#2 0x0000006557735570 in ?? ()
#3 0x00000003e167f5b6 in ?? ()
#4 0x00007ffeccfd8200 in ?? ()
#5 0x00000000004006cb in wrapper2(int, char*) ()
Cannot access memory at address 0x43676e6968746f56
(gdb) i r rsp rbp
rsp 0x7ffeccfd81c8 0x7ffeccfd81c8
rbp 0x43676e6968746f4e 0x43676e6968746f4e
查看 rsp rbp 发现 rbp 小于 rsp,根据上节的总结,我们知道 rbp 的值是非法的。
查看下 rsp 的内容,尝试找到正确的 rbp:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
(gdb) x /32x $rsp
0x7ffeccfd81c8: 0x6f4e6e61 0x6f745374 0x57735570 0x00000065
0x7ffeccfd81d8: 0xe167f5b6 0x00000003 0xccfd8200 0x00007ffe
0x7ffeccfd81e8: 0x004006cb 0x00000000 0xccfd979d 0x00007ffe
0x7ffeccfd81f8: 0xe0a97890 0x00000002 0xccfd8220 0x00007ffe
0x7ffeccfd8208: 0x004006f1 0x00000000 0xccfd979d 0x00007ffe
0x7ffeccfd8218: 0x00000000 0x00000001 0xccfd8240 0x00007ffe
0x7ffeccfd8228: 0x00400727 0x00000000 0xccfd8328 0x00007ffe
0x7ffeccfd8238: 0x00000000 0x00000002 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x7ffeccfd8200, 0x00007ffeccfd979d, 0x00007ffeccfd8220, 0x00007ffeccfd8240, 0x00007ffeccfd8328 都大于 0x7ffeccfd81c8,info symbol 这三个地址的下个单元地址看看能否正常显示函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
(gdb) info symbol 0x004006cb
wrapper2(int, char*) + 36 in section .text of test
(gdb) info symbol 0xe0a97890
No symbol matches 0xe0a97890.
(gdb) info symbol 0x004006f1
wrapper3(int, char*) + 36 in section .text of test
(gdb) info symbol 0x00400727
main + 52 in section .text of test
可以看到 0x7ffeccfd8200, 0x00007ffeccfd8220, 0x00007ffeccfd8240 都可以正常显示下个单元的地址,结论 1 和 2都满足,接下来看看第 3 个结论是否也满足:
1
2
3
4
5
6
(gdb) x /2x 0x7ffeccfd8200
0x7ffeccfd8200: 0xccfd8220 0x00007ffe
(gdb) x /2x 0x00007ffeccfd8220
0x7ffeccfd8220: 0xccfd8240 0x00007ffe
(gdb) x /2x 0x00007ffeccfd8240
0x7ffeccfd8240: 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x7ffeccfd8200 刚好指向 0x00007ffeccfd8220,0x00007ffeccfd8220 也刚好指向 0x00007ffeccfd8240。所以这三个都是合法的 rbp。这样我们已经恢复了真实的调用栈:
1
2
3
wrapper2(int, char*) + 36 in section .text of test
wrapper3(int, char*) + 36 in section .text of test
main + 52 in section .text of test
看看 wrapper2 的汇编:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
(gdb) disassemble wrapper2
Dump of assembler code for function _Z8wrapper2iPc:
0x00000000004006a7 <+0>: push %rbp
0x00000000004006a8 <+1>: mov %rsp,%rbp
0x00000000004006ab <+4>: sub $0x10,%rsp
0x00000000004006af <+8>: mov %edi,-0x4(%rbp)
0x00000000004006b2 <+11>: mov %rsi,-0x10(%rbp)
0x00000000004006b6 <+15>: addl $0x1,-0x4(%rbp)
0x00000000004006ba <+19>: mov -0x10(%rbp),%rdx
0x00000000004006be <+23>: mov -0x4(%rbp),%eax
0x00000000004006c1 <+26>: mov %rdx,%rsi
0x00000000004006c4 <+29>: mov %eax,%edi
0x00000000004006c6 <+31>: callq 0x400681 <_Z8wrapper1iPc>
0x00000000004006cb <+36>: leaveq
0x00000000004006cc <+37>: retq
End of assembler dump.
可以看到这里返回地址为 0x00000000004006cb <+36>: leaveq。
从前面
1
0x7ffeccfd81e8: 0x004006cb 0x00000000 0xccfd979d 0x00007ffe
看到栈地址 0x7ffeccfd81e8 保存 wrapper1 的返回地址为 0x004006cb ,和 wrapper2 的汇编相符
,故继续看看 callq 0x400681 <_Z8wrapper1iPc>。
shell c++filt 查看下函数的原型:
1
2
(gdb) shell c++filt _Z8wrapper1iPc
wrapper1(int, char*)
看下 wrapper1 的汇编:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
(gdb) disassemble wrapper1
Dump of assembler code for function _Z8wrapper1iPc:
0x0000000000400681 <+0>: push %rbp
0x0000000000400682 <+1>: mov %rsp,%rbp
0x0000000000400685 <+4>: sub $0x10,%rsp
0x0000000000400689 <+8>: mov %edi,-0x4(%rbp)
0x000000000040068c <+11>: mov %rsi,-0x10(%rbp)
0x0000000000400690 <+15>: addl $0x1,-0x4(%rbp)
0x0000000000400694 <+19>: mov -0x10(%rbp),%rdx
0x0000000000400698 <+23>: mov -0x4(%rbp),%eax
0x000000000040069b <+26>: mov %rdx,%rsi
0x000000000040069e <+29>: mov %eax,%edi
0x00000000004006a0 <+31>: callq 0x400640 <_Z8overflowiPc>
0x00000000004006a5 <+36>: leaveq
0x00000000004006a6 <+37>: retq
End of assembler dump.
callq 0x400640 <_Z8overflowiPc> 之前都是 rbp rsp 操作,推测出执行 callq 0x400640 <_Z8overflowiPc> 时引起的栈溢出。
1
2
3
4
5
(gdb) x /16x $rsp
0x7ffeccfd81c8: 0x6f4e6e61 0x6f745374 0x57735570 0x00000065
0x7ffeccfd81d8: 0xe167f5b6 0x00000003 0xccfd8200 0x00007ffe
0x7ffeccfd81e8: 0x004006cb 0x00000000 0xccfd979d 0x00007ffe
0x7ffeccfd81f8: 0xe0a97890 0x00000002 0xccfd8220 0x00007ffe
0x7ffeccfd81c8 的内容本应该是 0x004006a5 0x00000000 (指向返回地址 x00000000004006a5 <+36>: leaveq),但由于栈溢出被覆盖了。因此猜测是 _Z8overflowiPc 函数引起的。
注:为什么是 0x7ffeccfd81c8?前面知道 0x7ffeccfd81e8 保存调用 wrapper1 的返回地址。由上图可以看出,调用 wrapper1 时, 减去 8 个字节的 push %rbp,减去 16 字节的局部变量(sub $0x10,%rsp),再减去 8 个字节的 callq 0x400640 <_Z8overflowiPc>,即 0x7ffeccfd81e8 - 32 = 0x7ffeccfd81c8f 保存调用 _Z8overflowiPc 的返回地址0x00000000004006a5
1
2
(gdb) shell c++filt _Z8overflowiPc
overflow(int, char*)
因此定位到 overflow 函数代码中用到 strcpy 导致溢出。