数据类型
Druid 每行包括三种类型的数据:
-
Timestamp
每行数据必须包括 timestamp,数据以 timestamp 进行分区。
-
Dimension
Dimension 可以执行 filter 或者 grouped by。
-
Metrics
Metrics 可以执行 aggregated 操作。通常是数值型的数据。
Bitmap Index 位图索引
考虑以下数据集:
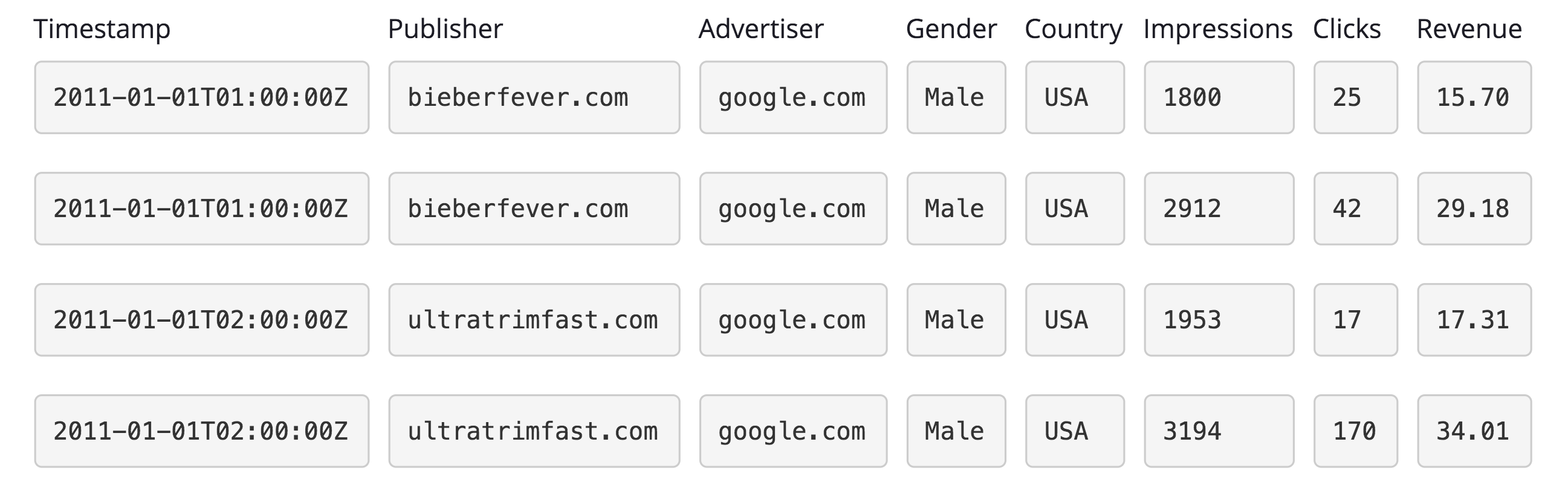
其中 Publisher、Advertiser、Gender 和 Country 为 dimension 列,而 Impressions、Clicks 和 Revenue 为 metrics 列。
我们可以用数组的形式来展示哪些行的 publisher 列为特定的 publisher:
bieberfever.com -> [1][1][0][0]
ultratrimfast.com -> [0][0][1][1]
即第 3、4 行的 publisher 为 bieberfever.com,第 1、2 行的 publisher 为 ultratrimfast.com。
从 dimension 列值到行的映射构成了倒排索引(inverted index)。查询哪些行包含了 bieberfever.com 或 ultratrimfast.com,只需要简单将两个数组执行 OR 操作:
[1][1][0][0] OR [0][0][1][1] -> [1][1][1][1]
因此数据检索中的 Where 操作,转化成 bitmap 的布尔操作。下一节简单介绍海量 bitmap 如何高效执行布尔操作。
高效 bitmap 布尔操作:bitmap 压缩
大多数运行长度编码算法(run-length encoding algorithms)用一个字来存储一连串的 0 或 1,其中包含了 0/1 串的长度,以及是 zero fill 还是 one fill。例如 Word-Aligned Hybrid(WAH) 压缩算法:
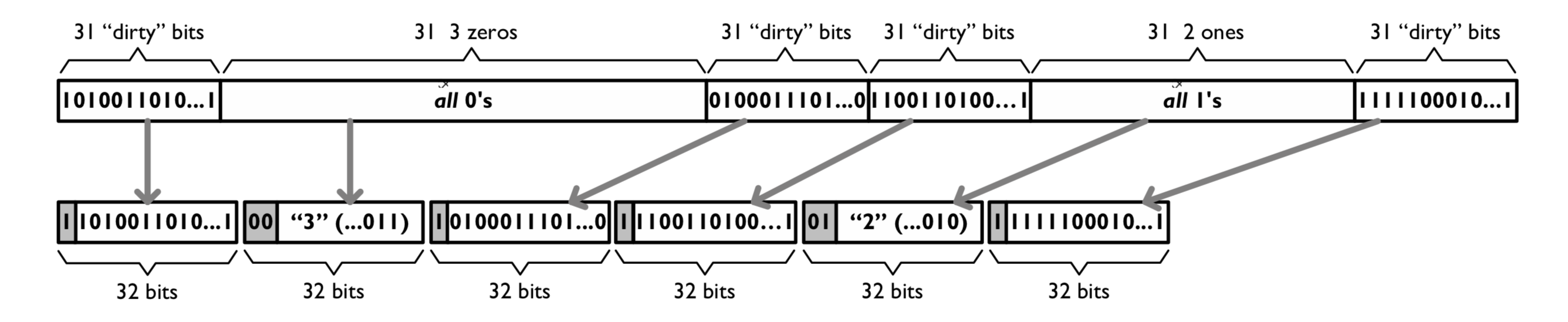
Concise 压缩算法引入了 mixed fill。Mixed fill 序列中头两个 bits 表示 fill 的类型,接下来 5 个 bits 可表示在哪个位置从 0 变成 1(或从 1 变成 0)。整数集 {3, 5, 31-93, 1024, 1028, 1040187422} 压缩后如下:
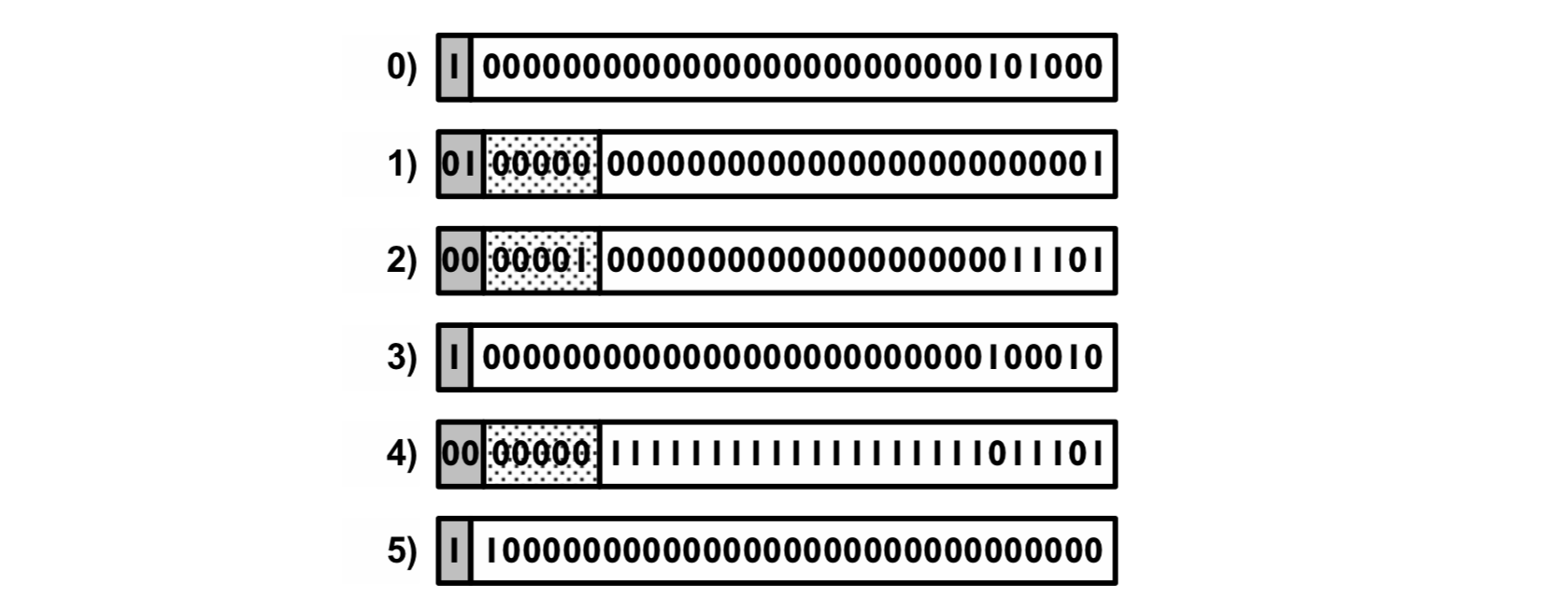
word #0 表示 0-30 范围的整数,word #1 表示 31-92 范围的整数,word #2 表示 93-1022 范围内的整数,word #3 表示 1023-1053 范围内的整数,word #4 表示 1054-1040187391 范围内的整数,word #5 表示 1040187392-1040187422 范围内的整数。
word #0、#3 和 #5 最左的 bit 位为 1,表示其为 literal words,剩下的 31 位为未压缩过的 31-bit block。word #1、#2 和 #4 最左位为 0,标识其为 fill words,第二位为 fill type(zero fill 还是 one fill),接下来 5 bits 为 position bits,表示在第一个 31-bit block 中 flipped bit 的位置。如果 position bits 为 00000,表示是 pure fill,类似于 WAH。00001 表示需要 flip rightmost bit,11111 表示需要 flip leftmost bit。
以 word #2:00|00001|0000000000000000000011101 为例:11101 十进制为 29,表示有 29 个 31-bit block。因此最后一个 31-bit block 的起始值为 93 + 29 * 31 即为 992,结束值为 992 + 30 即 1022(每个 31-bit block 表示 31 个数字)。因此 00|xxxxx|0000000000000000000011101 (暂时忽略 position bits)含义为 从 93 到 1022 都是 0 。Position bits 为 00001 表示需要排除掉 first 31-bit block 的 rightmost bits,也就是排除掉 93。因此 word #2 表示 94-1022 的 bits 都为 0。
另外 Roaring Bitmap 压缩算法在业界也很常用,值得一看。
参考文献
Maximum Performance with Minimum Storage: Data Compression in Druid